Workflows
Workflows constrain the Assistant to execute with a fixed set of tools, files, and context. Nomic has pre-built workflows for common project delivery tasks and also supports a workflow builder.
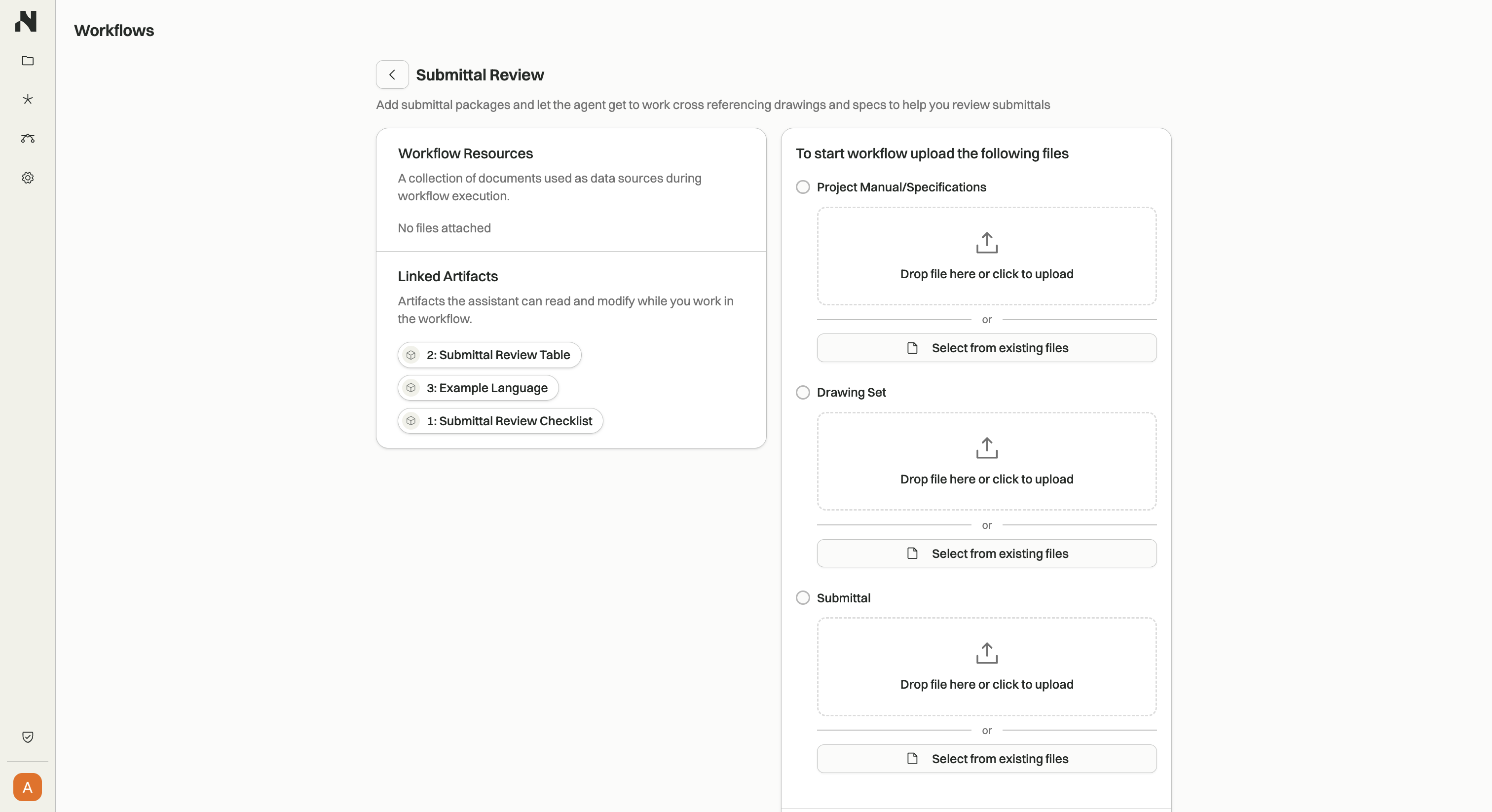
How Workflows Work
Workflows provide a structured way to solve specific project delivery tasks by constraining Assistant's capabilities. Each workflow defines:
- Fixed tools - A specific set of tool calls Assistant can use
- Defined files and context - Specific files, integrations, or data sources the workflow can access
- Task constraints - Boundaries that keep Assistant focused on the workflow's objective
This constraint-based approach ensures consistent, reliable results for repetitive project tasks like code compliance checks, submittal reviews, and QA/QC processes.
Pre-Built Workflows
Nomic provides pre-built workflows optimized for common project delivery tasks:
- Drawing Standards Check - Perform quality assurance and quality control checks on drawings and documentation
- Submittal Review - Review contractor submittals against project specifications and drawings
- Drawing Detail Search - Search past projects for similar drawings and examples to reference for your current work
- Code Compliance - Check drawings against building codes and standards with cited compliance results
Each pre-built workflow is configured with the right tools and context to deliver accurate, consistent results for its specific task. Learn how to customize these pre-built workflows or use them as a jumping off point for your own custom workflows in the Best Practices section.
Workflow Builder
Nomic supports a workflow builder that lets you create custom workflows tailored to your firm's specific needs:
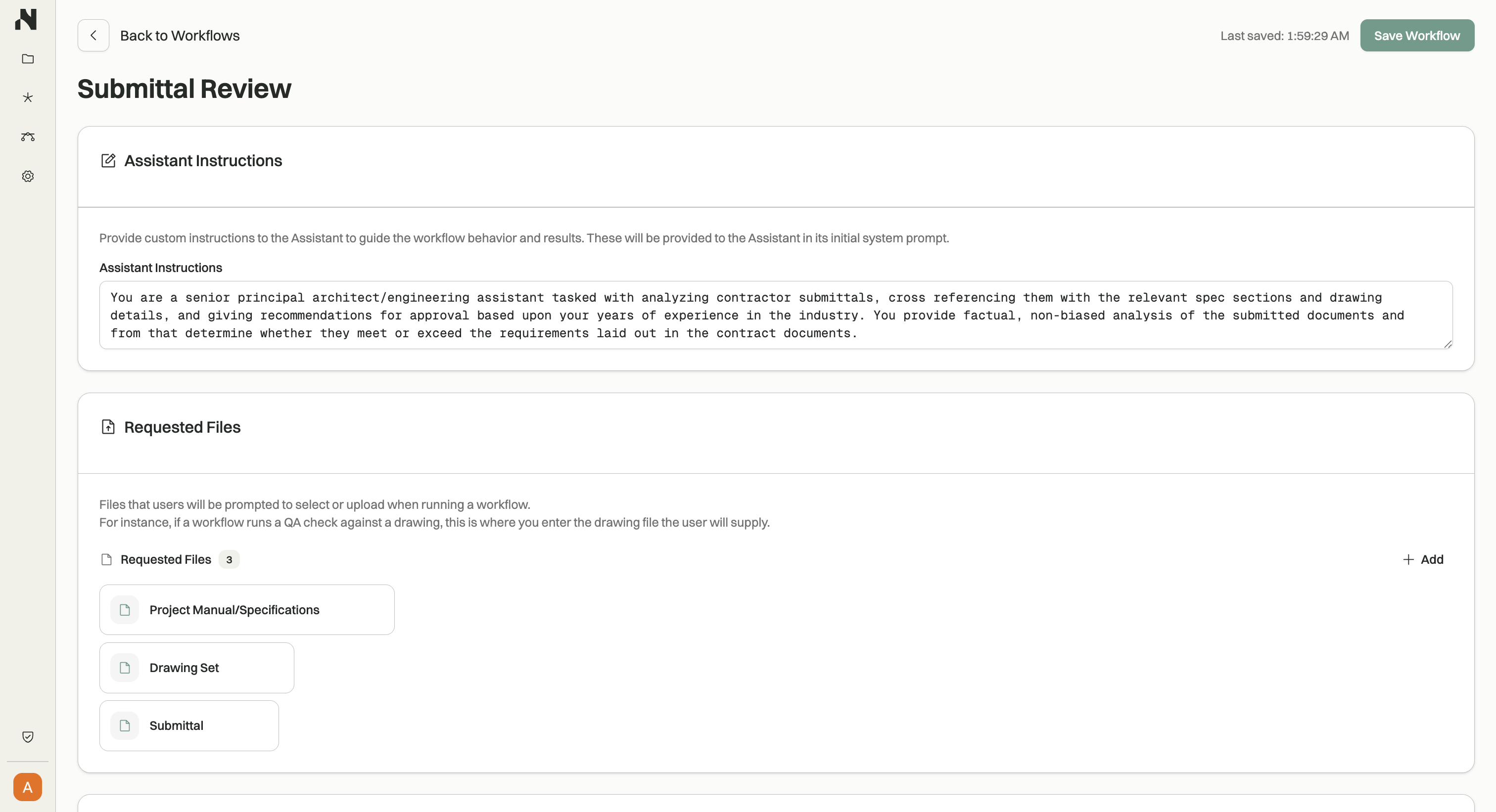
With the workflow builder, you can configure:
- Assistant Instructions - Provide custom instructions to guide the workflow behavior and results. These instructions are included in the Assistant's system prompt to ensure consistent, task-focused execution.
- Requested Files - Define files that users will be prompted to select or upload when running the workflow. For example, a QA workflow might request the drawing file to check.
- Working Artifacts - Specify files that Assistant can read from and write to during workflow execution. Artifacts can serve as scratch pads, checklists, or templates. For instance, a submittal review workflow might include a checklist of items to verify.
- Knowledge Base - Configure folders, files, and tagged collections that Assistant will have access to while executing the workflow. This ensures the workflow has the right context from your project data.
- Publish Settings - Set workflows as public (visible to all users in your organization with a shareable link) or private (only visible to you).
Custom workflows enable you to automate firm-specific processes and standardize how Assistant handles your unique project delivery tasks. See the Best Practices guide for tips on creating effective custom workflows.
Getting Started
To start using workflows:
- Choose a workflow - Select a pre-built workflow that matches your task, or use the workflow builder to create a custom one
- Configure context - Ensure the workflow has access to the files and data it needs through integrations or direct uploads
- Run the workflow - Execute the workflow to get consistent, reliable results for your project task
For detailed setup instructions, see the Quickstart guide or visit the Admin section to configure integrations.